
In the field of plastic, rubber, and food processing, choosing the right type of screw extruder can be the difference between optimal production efficiency and costly downtime. Many users struggle with inconsistent product quality, energy inefficiency, or throughput limitations, often because they’re using the wrong type of extruder for their specific material or process. Understanding the different types of screw extruders and their unique applications is essential for engineers, production managers, and procurement teams to make informed decisions and streamline production.
There are three main types of screw extruders: single-screw, twin-screw (co-rotating and counter-rotating), and multi-screw extruders. Single-screw extruders are best for general-purpose use and consistent materials, while twin-screw extruders excel in mixing, compounding, and devolatilization. Multi-screw extruders, though less common, are specialized for extremely high throughput and advanced material blending.
Whether you're extruding pet food, plastics, bio-resins, or pharmaceuticals, choosing the right extruder depends on your material properties, process goals, and the level of mixing or shearing required. Keep reading as we break down each type of screw extruder, their configurations, advantages, and how they compare in real industrial settings.
\
Twin-screw extruders provide better mixing than single-screw extruders.True
Twin-screw extruders allow intermeshing screw profiles that enhance shear, distributive, and dispersive mixing.
\
Single-screw extruders are always more energy-efficient than twin-screw models.False
While single-screw extruders often use less energy per unit, twin-screw extruders can process materials more quickly and with higher uniformity, which can offset energy use.
🛠️ Classification of Screw Extruders
1. Single-Screw Extruders
Single-screw extruders are the most commonly used type in various industries due to their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance. They consist of one rotating screw inside a cylindrical barrel. They are ideal for continuous processes such as extrusion of thermoplastics, rubber, and even food like pasta or snacks.
Applications:
- Plastic compounding
- Film and pipe production
- Dry pet food processing
- Rubber profile extrusion
Pros:
- Lower capital cost
- Simple operation and cleaning
- Suitable for homogenous materials
Cons:
- Limited mixing capacity
- Not ideal for reactive or highly filled systems
| Parameter | Single-Screw Extruder |
|---|---|
| Mixing Capability | Low to Medium |
| Material Compatibility | Limited to homogenous materials |
| Maintenance Cost | Low |
| Throughput | Medium |
| Complexity | Low |
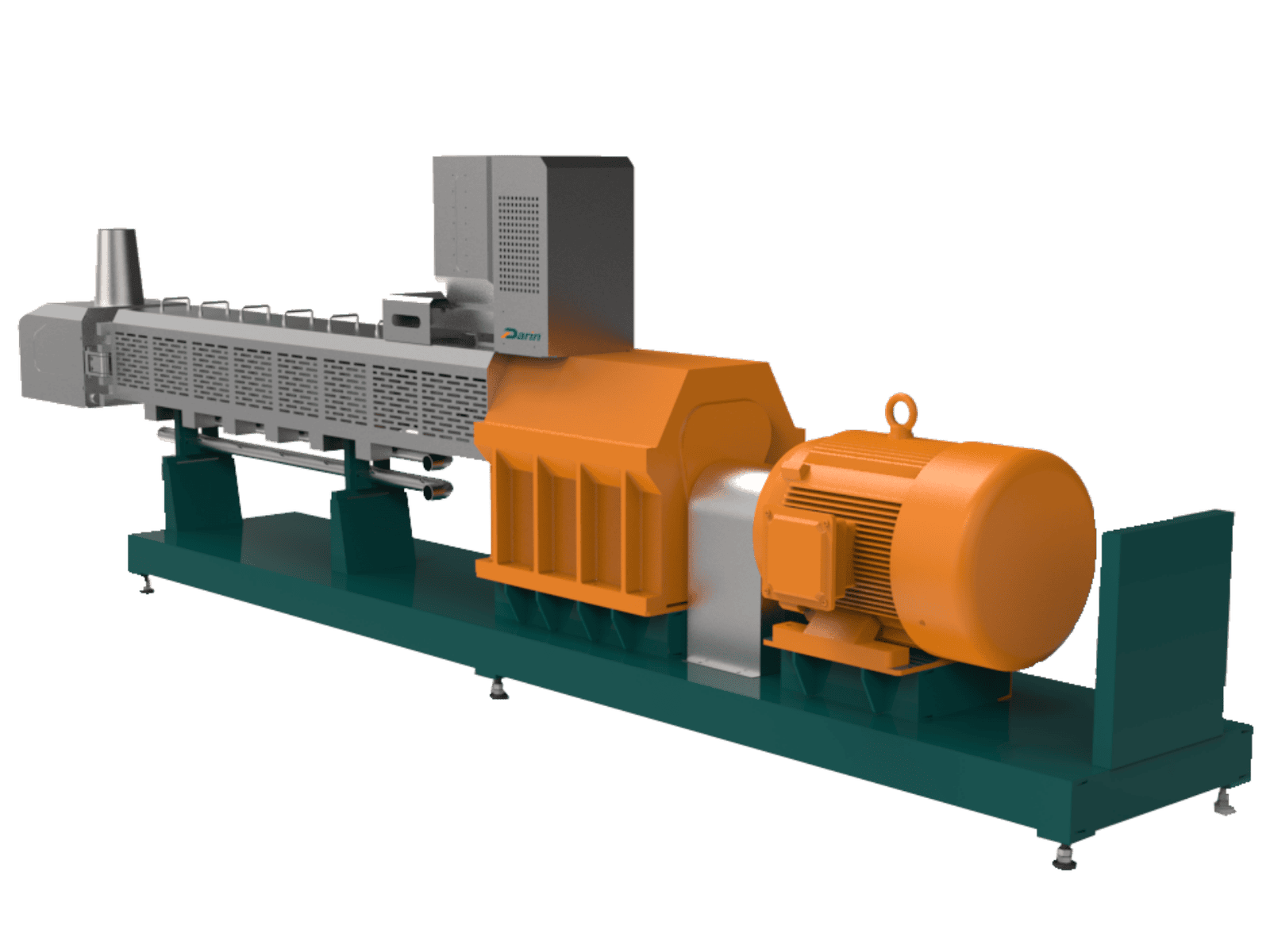
2. Twin-Screw Extruders
Twin-screw extruders use two parallel screws that rotate inside the same barrel. They can be either co-rotating (both screws rotate in the same direction) or counter-rotating (rotate in opposite directions). These are widely used in food, chemical, polymer, and pharmaceutical industries.
Co-Rotating Twin-Screw:
- Best for compounding, devolatilization, and shearing tasks.
- Highly modular and flexible.
Counter-Rotating Twin-Screw:
- Better for de-aeration and direct forming.
- Typically used in PVC processing and profile extrusion.
Applications:
- Wet pet food and treats
- Masterbatch production
- Bioplastics and recycling
- Pharmaceutical pelletizing
Pros:
- Superior mixing and kneading
- Handles heat-sensitive and high-viscosity materials
- Allows for process flexibility (e.g., venting, liquid addition)
Cons:
- Higher cost and complexity
- Requires skilled operators
| Feature | Co-Rotating Twin | Counter-Rotating Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Shear Force | High | Moderate |
| Material Feeding Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Application Flexibility | Broad | Moderate |
| Product Uniformity | Excellent | Good |
| Screw Speed (RPM) | High (300–1200) | Lower (10–100) |

3. Multi-Screw and Special Screw Extruders
These advanced systems include triple-screw and even quadruple-screw extruders used for very high throughput or highly specialized mixing tasks. They are typically custom-built for niche industrial applications and R\&D purposes.
Variants:
- Tri-screw extruders: Extra screw improves mixing and throughput.
- Planetary extruders: One main screw with several satellite screws rotating around it.
Applications:
- Ultra-high output food extrusion
- Sensitive pharmaceutical formulations
- High-filler masterbatches
| Extruder Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Triple-Screw | High-output food & plastic compounding | Enhanced distributive & dispersive mix |
| Planetary Screw | Heat-sensitive food/pharma mixing | Low shear, high surface renewal |
| Tandem Extruder | Multi-stage processing | Enables staged reactions or transitions |
🧩 Choosing the Right Extruder: Decision-Making Guide
Selecting the correct screw extruder involves multiple variables, including material type, throughput requirements, heat sensitivity, shear sensitivity, and desired product characteristics. The table below provides a quick comparison guide:
| Criteria | Single-Screw | Twin-Screw (Co) | Twin-Screw (Counter) | Multi-Screw |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Variety | Limited | Wide | Moderate | Niche-specific |
| Mixing Performance | Low | Excellent | Good | Highest |
| Processing Flexibility | Moderate | Very High | Medium | Custom |
| Throughput | Medium | High | Medium | Very High |
| Cost | Low | High | High | Very High |
📈 Real-World Performance Data (Throughput vs Energy Use)
Below is a performance comparison chart showing the relative energy consumption vs. output efficiency of common extruder types in food and plastic applications.

🏁 Conclusion
Each type of screw extruder has its strengths and ideal use cases. Single-screw extruders are perfect for standard, simple applications, while twin-screw systems dominate where performance, flexibility, and precision are required. For manufacturers facing unique challenges or very high-output requirements, multi-screw or custom designs can provide the ultimate solution.
📞 Contact Darin Machinery Today
As a leading manufacturer of advanced extruders for the food and pet food industries, Darin Machinery offers a wide range of high-performance single-screw and twin-screw extrusion lines tailored to your needs. Whether you're processing kibble, snacks, or specialty formulations, our expert engineers can help you design and implement the ideal solution.
👉 Visit www.petreatsmachine.com to explore our products.
📩 Get in touch now to discuss your extrusion requirements and receive a custom quote.
5. FAQ
Q1: What are the main types of screw extruders?
A1: The main types of screw extruders are single-screw extruders, twin-screw extruders (co-rotating and counter-rotating), and multi-screw or specialty extruders. Each type varies in configuration, material handling, mixing capability, and application. Single-screw is ideal for simple operations, while twin-screw extruders offer better mixing and versatility for complex formulations.
Q2: How does a single-screw extruder differ from a twin-screw extruder?
A2: A single-screw extruder uses one rotating screw in a barrel to convey and melt material, typically used for uniform materials like thermoplastics. Twin-screw extruders use two screws, offering superior mixing, self-wiping action, and suitability for processing materials that require high shear, accurate control, or reaction capability.
Q3: What are co-rotating and counter-rotating twin-screw extruders?
A3: Co-rotating twin-screw extruders have screws rotating in the same direction, promoting efficient mixing and high throughput. Counter-rotating extruders have screws turning in opposite directions, providing lower shear, precise control, and are commonly used for PVC and heat-sensitive compounds.
Q4: Are there any specialty screw extruders?
A4: Yes, specialty screw extruders include planetary extruders, multi-screw extruders, conical twin-screw extruders, and reciprocating screw extruders. These are tailored for niche applications like ultra-precise compounding, devolatilization, or gentle processing of delicate materials.
Q5: How do I select the right type of screw extruder for my process?
A5: Selection depends on material characteristics, throughput requirements, level of mixing needed, and product application. For simple thermoplastics, single-screw extruders suffice. For complex blends, reactive extrusion, or high output needs, twin-screw or specialty extruders are more appropriate. Consulting an extrusion expert helps optimize system performance.
6. References
- Types of Extruders – https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/extruder – ScienceDirect
- Single vs Twin-Screw Extruders – https://www.ptonline.com/articles/choosing-between-single-and-twin-screw-extruders – Plastics Technology
- Twin-Screw Extruder Designs – https://www.coperion.com/en/products-solutions/extruders/ – Coperion
- Conical Twin-Screw Extruders – https://www.battenfeld-cincinnati.com/en/extruders/conical-twin-screw – Battenfeld-Cincinnati
- Planetary Extruders – https://www.leistritz.com/en/extruders/planetary-roller-extruders – Leistritz
- Polymer Extrusion Overview – https://polymerdatabase.com/polymer%20processing/Extrusion.html – Polymer Database
- Plastic Extrusion Guide – https://www.extru-techinc.com/plastic-extrusion-basics – Extru-Tech
- Food Extrusion Techniques – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9781119114833 – Wiley Online Library
- Extruder Selection Tips – https://www.thermofisher.com/blog/materials/choosing-the-right-extruder – Thermo Fisher
- Overview of Extrusion Processes – https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=16287 – AZoM Materials








