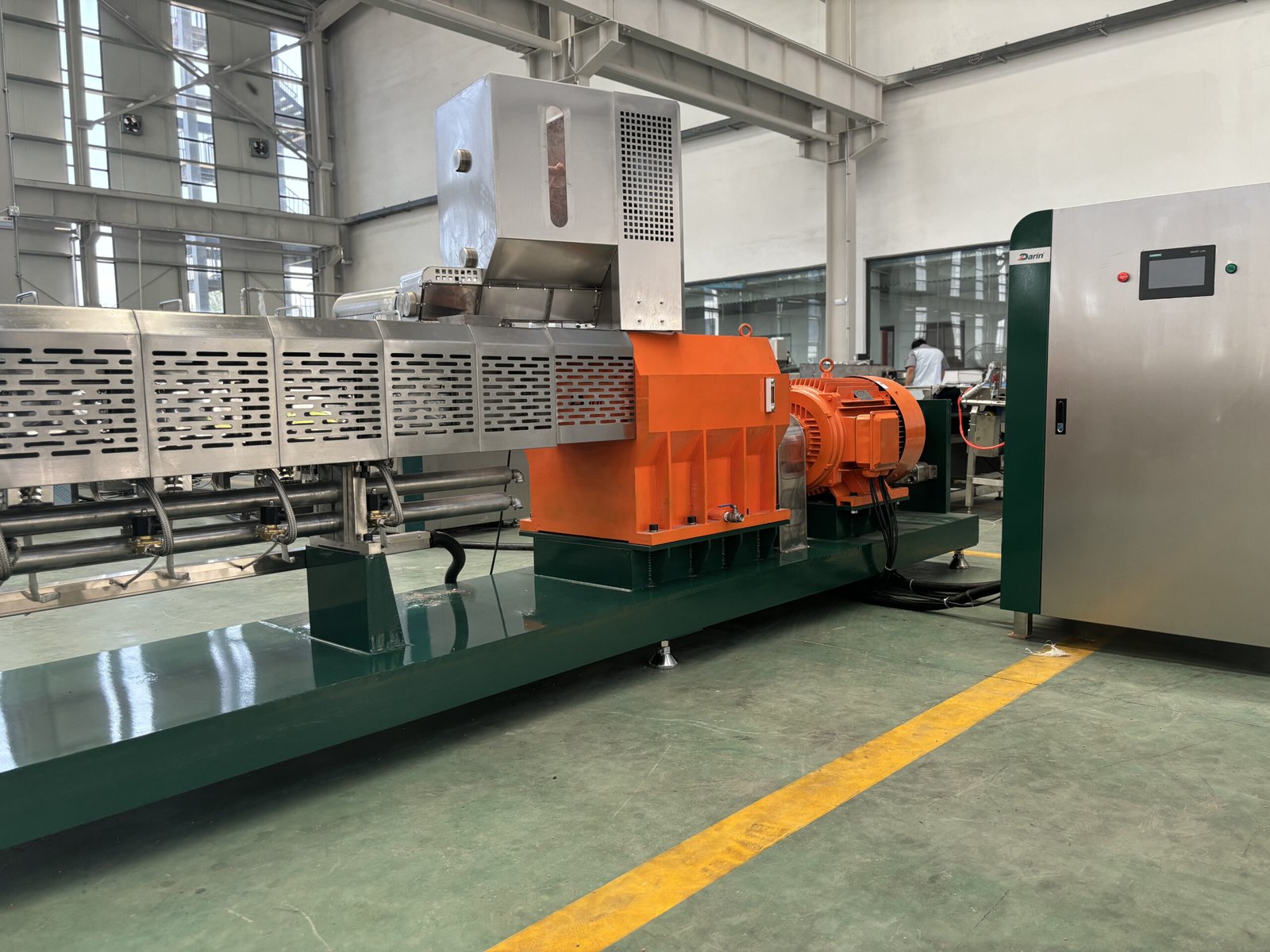
Powering a pet food extruder isn’t as simple as plugging into a standard outlet—this is heavy-duty industrial equipment that demands high, stable, and efficient electrical input to run motors, heaters, hydraulic units, and control systems. Choosing or installing the wrong power supply can result in erratic machine behavior, overheating, failed components, or even fire hazards. Power supply requirements vary depending on the extruder size, motor configuration, and production capacity, but all models demand precise voltage, frequency, and amperage setups to ensure consistent performance. In this guide, we’ll detail the exact power supply specifications needed for pet food extruders and how to plan your facility’s infrastructure accordingly.
Pet food extruders typically require a three-phase power supply of 380V to 480V at 50Hz or 60Hz, with total installed power ranging from 15 kW for pilot models to over 300 kW for large-scale industrial systems. The system includes motors for extrusion, feeders, cutters, heaters, and auxiliary devices—all requiring stable, high-capacity electrical input.
This isn't a one-size-fits-all scenario. Whether you’re running a compact R&D extruder or a full-scale 10-ton/hour production line, you must match your facility’s power infrastructure to the extruder’s exact requirements. Read on to discover what that entails.
Pet food extruders can be powered using standard single-phase household electricity.False
Pet food extruders require three-phase industrial electricity, typically 380V or 480V, to power high-capacity motors and heating elements. Single-phase power is insufficient for their operational needs.
Complete Power Supply Requirements for Pet Food Extruders
1. Electrical Input Specifications by Machine Size
| Extruder Size | Power Supply Requirement | Total Installed Power (kW) | Phase/Voltage/Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot-scale (<200 kg/h) | 15–25 kW | 3-phase, 380V, 50Hz | Optional 220V/60Hz for small labs |
| Medium-scale (300–1000 kg/h) | 40–90 kW | 3-phase, 380V/400V/415V | 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Industrial-scale (1–5 tons/h) | 120–200 kW | 3-phase, 400V–480V | Typically 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Large industrial (>5 tons/h) | 250–400 kW | 3-phase, 440V–480V | High amperage, may require transformer |
Important: The power specification may vary depending on the country (EU, US, Asia), so local compliance and panel compatibility must be confirmed before purchase.
2. Main Power Consumers in an Extruder Line
Each component in the extrusion line contributes to the total power load:
| Component | Typical Power (kW) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Main extrusion motor | 30–160 kW | Drives the screw shafts |
| Feeder motor | 0.5–5 kW | Controls feed rate |
| Preconditioner motor | 2–10 kW | Powers paddle mixing and steam injection |
| Cutter motor | 0.5–5 kW | Variable speed for shaping |
| Heating elements (barrel) | 5–30 kW | Steam or electric; controls temperature |
| Vacuum or air systems | 1–10 kW | Optional for venting or cooling |
| Control cabinet & PLC | 1–3 kW | Low-load but must be stable |
| Auxiliary equipment (dryer, coater, cooler) | 20–150+ kW | Often highest consumption outside extruder |
Case Example:
A 3 T/H twin-screw extruder system with integrated dryer and coater may have:
- Extruder: 110 kW
- Dryer: 80 kW
- Cooling: 15 kW
- Total installed: ~210–250 kW
3. Voltage, Frequency, and Phase Requirements
Most extruders are built to run on three-phase AC power, which delivers smoother, more efficient energy to high-load motors.
| Region | Common Voltage | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Europe | 380V / 400V | 50Hz |
| USA | 460V / 480V | 60Hz |
| Asia | 380V / 415V | 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Custom builds | 220V, 240V, 440V | Optional |
Transformer Use:
If your site has incompatible voltage, a step-up or step-down transformer may be needed to match the extruder’s input requirements.
4. Control Cabinet and Wiring Safety
Extruders are delivered with a central control cabinet that houses:
- Circuit breakers
- VFDs (Variable Frequency Drives)
- PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers)
- Overload protection systems
- Emergency stop (E-Stop) circuits
All wiring must meet:
- IP65/IP67 standards (for moisture and dust protection)
- CE, UL, or CSA certifications depending on region
- Shielded cables for sensor and control line protection
| Chart: Main Electrical Cabinet Layout |
|---|
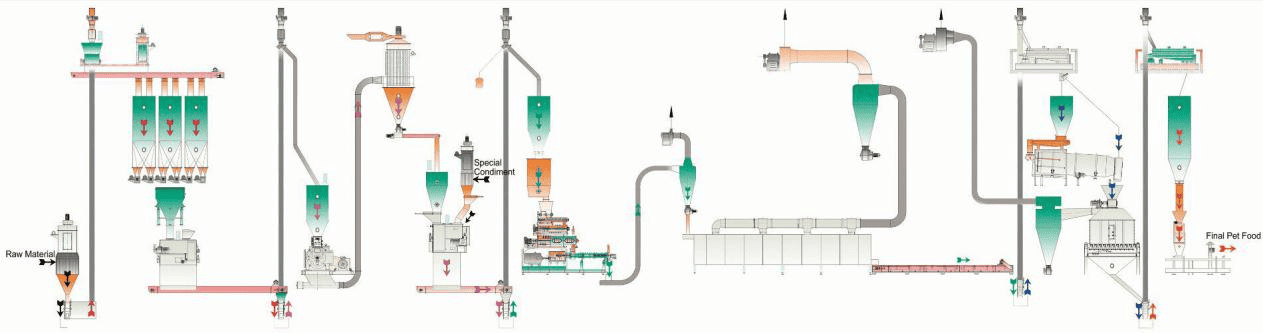
5. Power Infrastructure Planning Tips
To ensure safe and stable operation, follow these guidelines:
| Planning Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Circuit capacity | At least 20% higher than peak load |
| Wiring gauge | Use 4–70 mm² cables depending on amperage |
| Grounding | Mandatory earth grounding for all metallic parts |
| Surge protection | Required to prevent VFD or PLC damage |
| Isolation transformer | Optional for voltage stability and noise reduction |
6. Energy Efficiency and Load Management
Modern extruders support energy-saving features:
- VFD-controlled motors: Adjust power consumption based on load
- Auto shutdown timers: Turn off unused components
- Heat recovery: Reuse waste heat from dryer or extruder barrel
- Smart PLC logic: Optimize motor torque and heater usage
These features can reduce power consumption by 10–20% annually, especially in high-output plants.
7. Backup and Emergency Power Considerations
For facilities where downtime is unacceptable, backup power strategies are recommended:
| Option | Application |
|---|---|
| UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) | PLC, SCADA, critical sensors |
| Diesel or gas generator | Main drive motors and heating |
| Battery bank + inverter | Temporary control backup for safe shutdown |
Conclusion
The power supply requirements for pet food extruders are substantial and must be precisely matched to your equipment’s specifications. Most systems require three-phase, 380V to 480V at either 50Hz or 60Hz, with total power needs ranging from 15 kW to over 300 kW. In addition to the extruder itself, power must support auxiliary components like dryers, feeders, and cutters. A well-designed electrical infrastructure ensures stable production, safety compliance, and machine longevity. Whether you're starting with a compact lab machine or running a high-throughput factory, proper power planning is essential.
Need Help Matching the Right Power Supply?
Contact our technical team to review your facility’s electrical setup and ensure it meets your extruder’s power requirements. We provide:
- Custom power consumption charts
- Electrical drawings and installation guidance
- Transformer and panel configuration services
Let’s get your extruder running safely and efficiently—reach out today!
 Darin customer
Darin customer
FAQ
Q1: What type of power supply does a pet food extruder typically require?
A1: Pet food extruders generally require a 3-phase industrial power supply, commonly rated at 380V, 400V, or 460V depending on the region. The frequency is usually 50Hz or 60Hz, and power consumption varies based on the size and output of the extruder.
Q2: What is the typical power consumption range of pet food extruders?
A2: Power consumption for small-scale extruders can range from 15 kW to 50 kW. Medium to large-scale industrial extruders may require 75 kW to over 300 kW, especially when running high-output systems with additional auxiliary equipment like dryers and coolers.
Q3: Why do pet food extruders use 3-phase power?
A3: Three-phase power is used because it offers more efficient energy delivery, better motor performance, and higher load capacity. This is essential for powering large motors, heating elements, and automated systems in industrial-grade extruders.
Q4: Can pet food extruders run on single-phase electricity?
A4: No, standard industrial pet food extruders cannot operate on single-phase electricity due to their high power demand. However, very small or lab-scale extruders may be designed for single-phase use, but they offer limited capacity and functionality.
Q5: Are there energy-efficient models of pet food extruders?
A5: Yes, modern extruders come with energy-saving features such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), high-efficiency motors, and optimized thermal insulation. These features reduce energy waste and improve overall processing efficiency.
 Darin exhibition
Darin exhibition
References
- Electrical Design for Industrial Equipment - https://www.abb.com - ABB Group
- Energy Efficiency in Extrusion Systems - https://www.clextral.com/energy-efficiency/ - Clextral
- Variable Frequency Drives for Food Equipment - https://www.schneider-electric.com/en/product-range/533-variable-speed-drives/ - Schneider Electric
- Industrial Power Systems Overview - https://electrical-engineering-portal.com - EEP
- Choosing Power Supply for Machinery - https://www.automationdirect.com - AutomationDirect
- Pet Food Processing Power Analysis - https://www.petfoodindustry.com/articles/11235-energy-demand-in-pet-food-extrusion - Pet Food Industry
- Extruder Energy Optimization Guide - https://www.energy.gov - U.S. Department of Energy
- Safe Electrical Setup for Food Equipment - https://www.nfpa.org - National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)











