Inconsistent product quality, high waste, and frequent equipment breakdowns are major pain points for food manufacturers using extrusion technology without fully understanding how it works. These issues can severely impact production efficiency, increase operating costs, and reduce product appeal on the market. Fortunately, a thorough understanding of food extruder working principles allows operators and engineers to fine-tune parameters, improve consistency, and extend machine lifespan. This article offers a comprehensive breakdown of how food extruders work—from raw input to final product—along with technical insights and operational optimization.
A food extruder works by using one or more rotating screws to push food material through a heated barrel, where it is mixed, cooked under pressure, and shaped through a die to create a specific texture or form. The process combines mechanical shearing, thermal energy, and pressure to transform raw ingredients into uniform, stable, and ready-to-package food products.
This basic explanation only scratches the surface. To effectively leverage extrusion technology in food manufacturing, you’ll need to understand the mechanical sequence, component functions, and critical processing variables involved. Keep reading for a deeper technical dive.
A food extruder primarily cooks and shapes food using heat and pressure.Vrai
Extruders apply thermal and mechanical energy to mix, cook, and form food materials through a shaping die.
Understanding the Core Components of a Food Extruder
A food extruder consists of several integrated components that operate in a sequential and controlled manner:
| Composant | Fonction |
|---|---|
| Alimentateur | Introduces raw materials (e.g., flours, starches, proteins) into the barrel. |
| Vis(s) | Rotates to push, compress, and mix the material. Can be single or twin-screw. |
| Tonneau | Heated cylindrical chamber that houses the screw and regulates temperature. |
| Tête de filière | Shapes the final extruded product (e.g., puffed snacks, pasta, kibble). |
| Cutter | Cuts the extrudate into desired sizes upon exit from the die. |
| Système de contrôle | Adjusts speed, temperature, and pressure for process optimization. |
Types d'extrudeuses
| Type | Caractéristiques | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Extrudeuse à vis unique | One rotating screw, simpler control, cost-effective. | Breakfast cereals, snack pellets |
| Extrudeuse à double vis | Two intermeshing screws, better mixing, more control. | Pet food, textured proteins, instant noodles |
| Co-Rotating | Screws rotate in the same direction for better conveyance. | High-volume food production |
| Contre-rotation | Screws rotate in opposite directions for enhanced shearing and mixing. | Complex recipes, high-fiber blends |
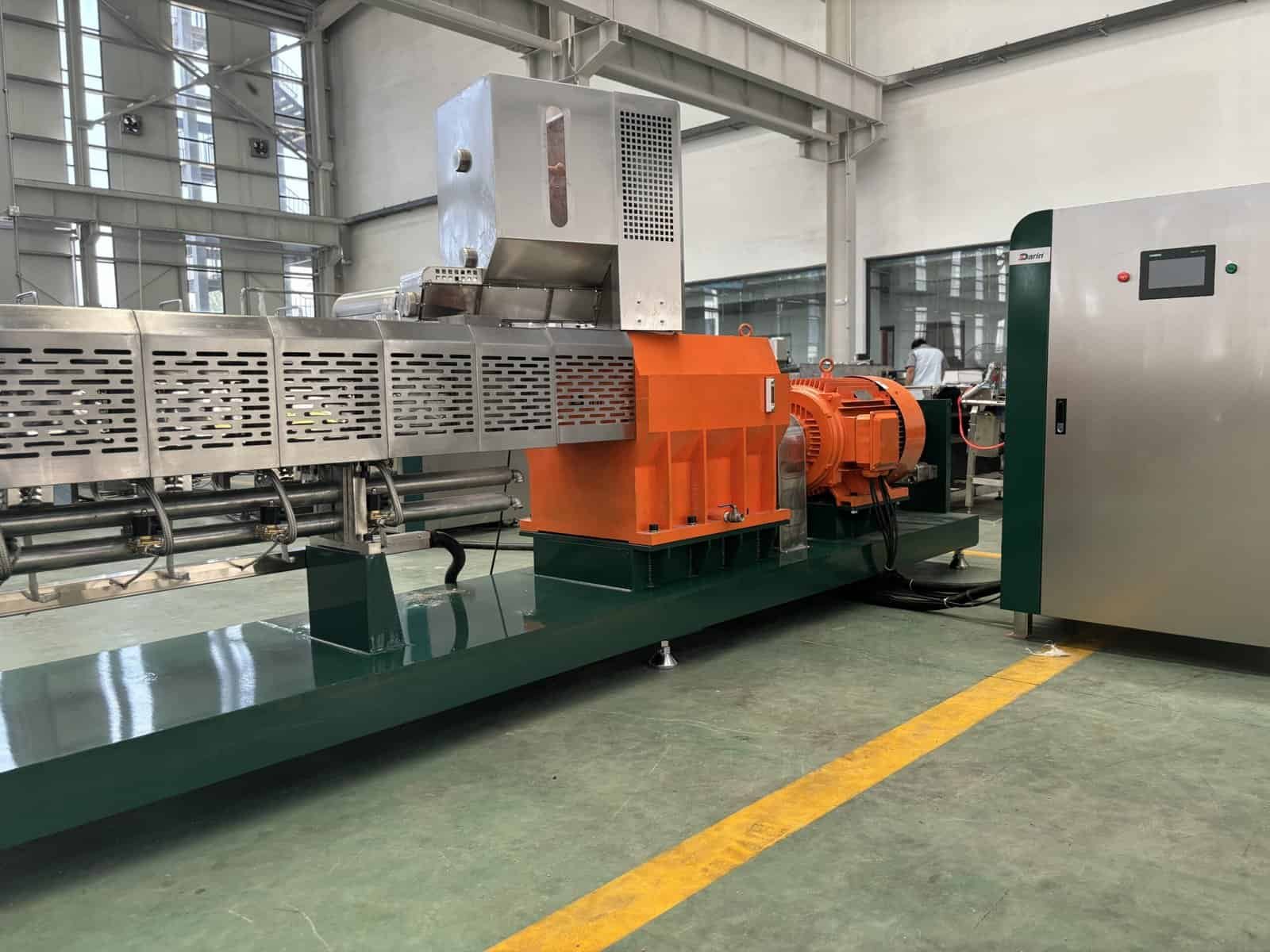

The Food Extrusion Process Step by Step
1. Feeding the Extruder
Raw food ingredients are blended into a homogeneous dry mix or dough. A volumetric or gravimetric feeder supplies this material into the extruder barrel.
2. Conveying and Mixing
The rotating screw(s) begin to transport the raw material forward through the barrel. As the screw turns:
- Material is compacted
- Frictional heat is generated
- Liquids can be injected (e.g., water, oil, steam)
- Shear mixing helps achieve a uniform mass
3. Chauffage et cuisson
Temperature zones along the barrel (via electric or steam jackets) bring the food to a precise cooking point. Thermomechanical energy causes:
- gélatinisation de l'amidon
- Dénaturation des protéines
- Water evaporation (for puffed products)
Temperature can range from 100°C to 200°C depending on the recipe.
4. Pressurization and Die Shaping
As the food material nears the end of the barrel:
- Pressure builds due to screw geometry and barrel design
- The cooked mass is forced through a die with specific hole shapes
- Sudden pressure drop causes flash expansion, creating puffed or porous textures
5. Cutting and Cooling
As the extrudate exits the die:
- A rotating cutter slices it into pellets, curls, or kibble
- Product is conveyed to a dryer or cooler to stabilize moisture and improve shelf life
Critical Control Parameters in Extrusion
| Paramètres | Impact sur le produit |
|---|---|
| Vitesse de la vis (tr/min) | Affects residence time, mixing intensity, shear level |
| Température du canon | Controls cooking degree, expansion rate, texture |
| Teneur en humidité | Influences plasticity, expansion, and final texture |
| Pression de la matrice | Regulates product density, smoothness, and output shape |
| Taux d'alimentation | Adjusts material throughput and processing consistency |
Case Study: Pet Food Extrusion at Darin Machinery
À Machines Darin, our high-capacity twin-screw extruders process pet food using the following parameters:
- Diamètre de la vis: 65mm–95mm
- Capacité de sortie: 200 kg/h to 2,000 kg/h
- Vitesse de la vis: Up to 600 rpm
- Temperature Zones: 5–8 independently controlled zones
- Applications: Dog food, cat food, fish feed, floating and sinking pellets
These machines incorporate advanced PLC+touchscreen controls for easy parameter adjustments and automated production tracking.
Why Choose Extrusion for Food Manufacturing?
Avantages :
- Polyvalence: Can process cereals, snacks, proteins, pet foods, baby foods
- Efficacité: Continuous operation with high throughput
- Uniformité: Consistent shape, moisture, and quality
- Personnalisation: Easily change dies to create new shapes
- Conception compacte: Integrates cooking, forming, and shaping in one machine
Limites :
- High initial cost for twin-screw systems
- Sensitive to moisture and ingredient fluctuations
- Requires skilled operation and maintenance
Example: Textured Vegetable Protein (TVP) Extrusion Flowchart
Raw Soy Flour + Water
↓
Preconditioning
↓
Twin-Screw Extrusion (Heating + Shear)
↓
Die Shaping → Texturized Chunks
↓
Drying and Cooling
↓
PackagingFood Products Made via Extrusion
| Produit | Type d'extrusion | Ingrédient clé | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|
| En-cas soufflés | Mono-vis | Corn, rice, potato | Airy, crispy |
| Céréales pour petit-déjeuner | Double vis | Maize, oat, wheat | Crispy, light |
| Croquettes pour animaux de compagnie | Double vis | Protein blends, grains | Crunchy, dense |
| TVP (Vegan Protein) | Double vis | Soy flour, pea protein | Fibrous, meat-like |
| Instant Noodles | Single-screw (cooked) | farine de blé | Elastic, chewy |
Résumé
Food extrusion is a versatile and highly efficient process that transforms raw food materials into value-added products by using a combination of heat, pressure, and mechanical shear inside a specially designed machine. Understanding how this system works—including its core components, control parameters, and product applications—empowers manufacturers to enhance product quality, reduce waste, and innovate with new food formats. Whether you're producing crunchy snacks, nutritious pet food, or plant-based proteins, extrusion offers unmatched flexibility and consistency in modern food manufacturing.
Ready to Upgrade Your Food Production Line?
Looking to implement or optimize extrusion in your food manufacturing business? Contact Machines Darin today for expert guidance, customized equipment solutions, and full after-sales support tailored to your production goals.

FAQ
Q1: What is the basic principle of a food extruder?
A1 : A food extruder works by pushing a food mixture through a barrel using one or more rotating screws. As the material moves forward, it is heated, pressurized, and sheared, then forced through a die to form specific shapes. The sudden drop in pressure at the die causes expansion and sets the final texture.
Q2: What are the main components of a food extruder?
A2: Key components include a nourrisseur, screw(s) (single or twin), baril, heating elements, die headet cutter system. These parts work together to mix, cook, and shape the raw materials into final food products.
Q3: What types of food products are made using extrusion?
A3: Extrusion is widely used to produce aliments à grignoter, breakfast cereals, pâtes, textured vegetable protein (TVP), aliments pour animauxet aquafeed. It allows consistent shape, taste, and texture across large batches.
Q4: How does temperature and pressure affect the extrusion process?
A4: High temperature (80–200°C) and pressure inside the barrel cook and gelatinize starches, denature proteins, and sterilize the material. These factors influence product texture, expansion, and digestibility, ensuring safe and uniform outcomes.
Q5: What is the difference between cold and hot extrusion in food processing?
A5: Hot extrusion involves cooking the food under high heat and pressure—ideal for pet food, cereals, and snacks. Cold extrusion shapes products without cooking, typically used for dough-based or refrigerated foods like cookie dough and meat snacks.
Références
- Food Engineering Magazine - https://www.foodengineeringmag.com
- Clextral Extrusion Technology - https://www.clextral.com
- Extru-Tech Inc. - https://www.extru-techinc.com
- ScienceDirect : Extrusion alimentaire - https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/food-science/extrusion
- Baker Perkins - https://www.bakerperkins.com
- AllAboutFeed - https://www.allaboutfeed.net
- Pet Food Processing - https://www.petfoodprocessing.net
- Wiley Online Library – Food Extrusion - https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com
- Feed Strategy Magazine - https://www.feedstrategy.com
- American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers - https://www.asabe.org










