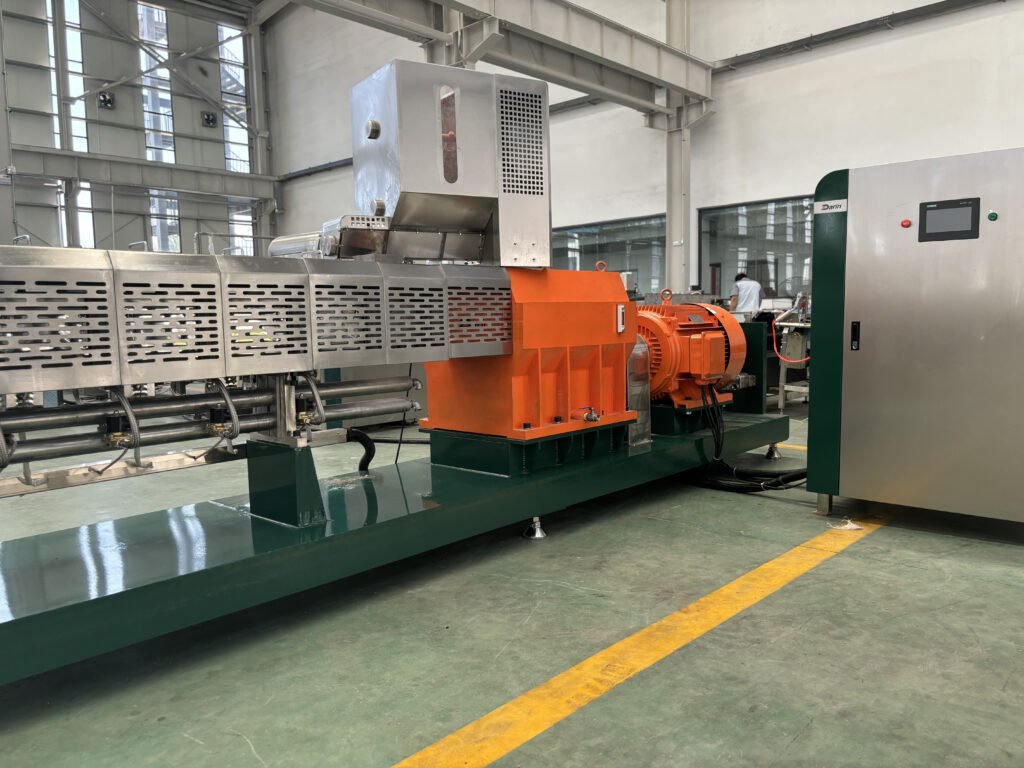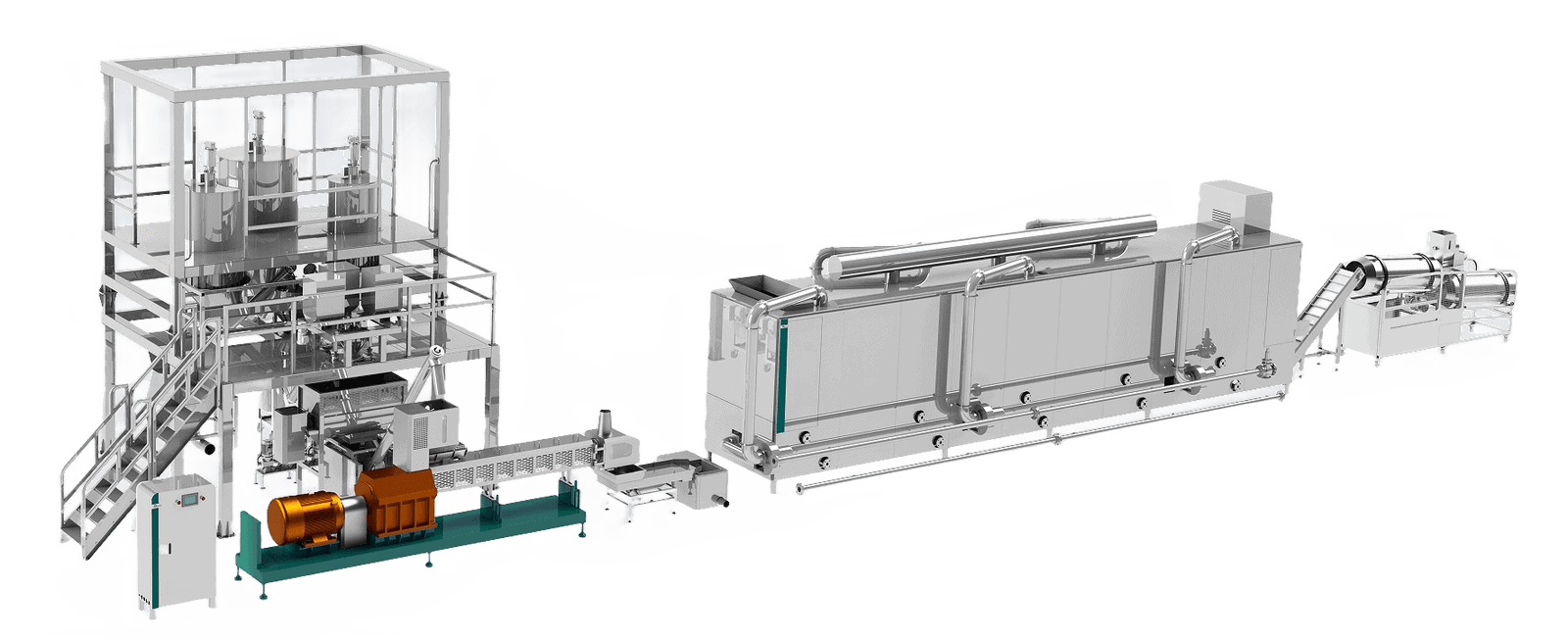
Food processing industries face increasing challenges in maintaining product uniformity, improving efficiency, and meeting consumer demand for high-quality pellet-based foods. Without advanced manufacturing processes like extrusion, food pellets can have inconsistent texture, nutritional loss, and inefficiency in mass production. The right extrusion process ensures consistency, enhanced digestibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Food extrusion for pellets is a continuous manufacturing process where raw ingredients are forced through a die under controlled heat, pressure, and moisture to form uniform pelletized food products. The process improves digestibility, texture, and shelf life of food while allowing for precise formulation of nutritional content.
If you are in the food manufacturing industry, understanding the pellet extrusion process is critical for optimizing production, improving product quality, and staying competitive. In this in-depth article, we will explore the various aspects of food extrusion, its types, equipment, raw materials, and technological advancements.
What Is Food Extrusion and How Does It Work?
Understanding the Extrusion Process
Food extrusion is a high-temperature, high-pressure process where raw materials are mixed, cooked, and shaped into a final product. The process occurs in an extruder, which consists of a barrel, screw system, and die, responsible for processing the food ingredients into uniform pellets.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Extrusion Process
- Raw Material Preparation – Ingredients such as grains, proteins, starches, and flavorings are pre-mixed.
- Feeding – The raw mixture is fed into the extruder through a hopper.
- Cooking & Mixing – The extruder screw moves and shears the material under high pressure and heat, gelatinizing starches and denaturing proteins.
- Shaping & Forming – The material passes through a die, shaping it into pellet forms.
- Cutting & Drying – A cutter trims the pellets to desired sizes, followed by drying to remove excess moisture and ensure shelf stability.
- Cooling & Packaging – The final product is cooled and packaged for distribution.
Why Is Extrusion Important?
- Enhances digestibility and palatability of food.
- Improves texture and appearance.
- Increases shelf life by reducing moisture.
- Ensures uniformity in product size and shape.
Food extrusion enhances nutritional quality and digestibility of pelletized products.True
The high-temperature and shear process breaks down complex molecules, making nutrients more bioavailable.
What Are the Types of Extrusion Processes for Food Pellets?
1. Cold Extrusion vs. Hot Extrusion
| Type | Temperature | Key Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Extrusion | < 100°C | Retains nutrients, used for softer products | Meat analogs, pasta, pet food |
| Hot Extrusion | > 100°C | Kills bacteria, increases digestibility | Cereal snacks, puffed products |
2. Single-Screw vs. Twin-Screw Extrusion
| Extrusion Type | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Screw | Cost-effective, simple design, easy maintenance | Limited ingredient flexibility |
| Twin-Screw | Higher precision, better mixing, higher efficiency | Higher initial cost |
Twin-screw extruders provide better control over texture and product consistency.True
Twin-screw extruders have intermeshing screws that enhance ingredient mixing and consistency.
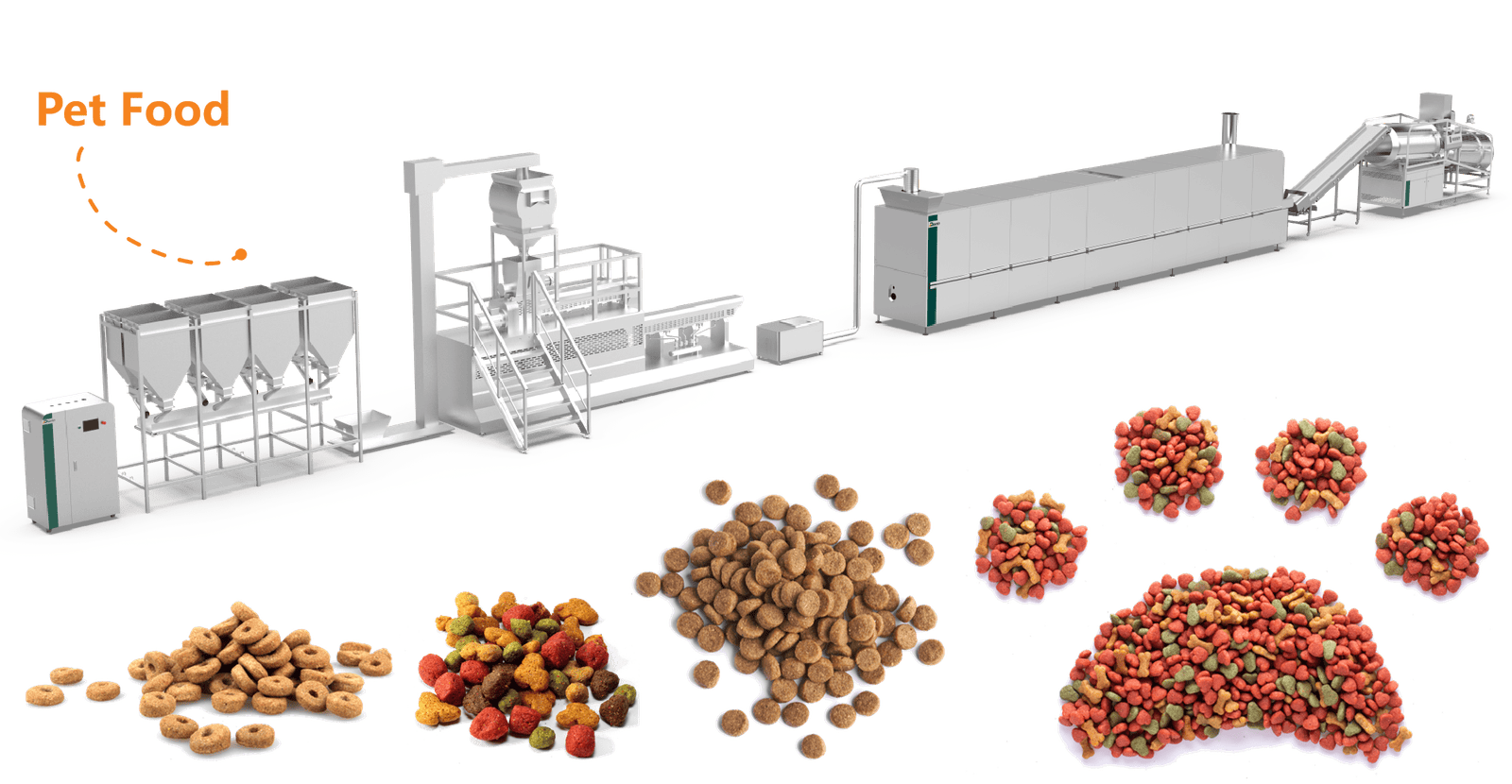

What Are the Main Components of an Extruder Machine?
Key Components of a Food Extruder
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Hopper | Feeds raw material into the system |
| Barrel | Houses the screw and applies heat |
| Screw(s) | Mixes and moves the material forward |
| Die | Shapes the final product |
| Cutter | Cuts extruded food into desired sizes |
How to Choose the Right Extruder?
- Consider throughput requirements.
- Choose screw design based on product type.
- Evaluate temperature control capabilities.
What Are the Key Ingredients in Pelletized Food Extrusion?
Common Raw Materials
| Ingredient | Function |
|---|---|
| Starches | Provides structure and crispiness |
| Proteins | Enhances texture and nutrition |
| Fats & Oils | Affects mouthfeel and shelf stability |
Impact of Ingredients on Extrusion Quality
- High starch content improves crispiness.
- Proteins affect expansion and chewiness.
- Moisture level controls pellet density.
How Does Extrusion Impact Food Quality and Nutrition?
Nutritional Advantages of Extruded Food
- Improved digestibility due to structural changes in proteins and starches.
- Lower microbial load due to high temperatures.
- Fortification options allow for customized nutrition.
Extrusion cooking reduces anti-nutritional factors in food ingredients.True
The process neutralizes harmful compounds like phytates and lectins.
What Are the Industrial Applications of Food Extrusion?
Industries Using Extruded Pellets
| Industry | Example Products |
|---|---|
| Breakfast Cereals | Cornflakes, granola clusters |
| Pet Food | Kibble, treats |
| Snacks | Chips, puffed snacks |
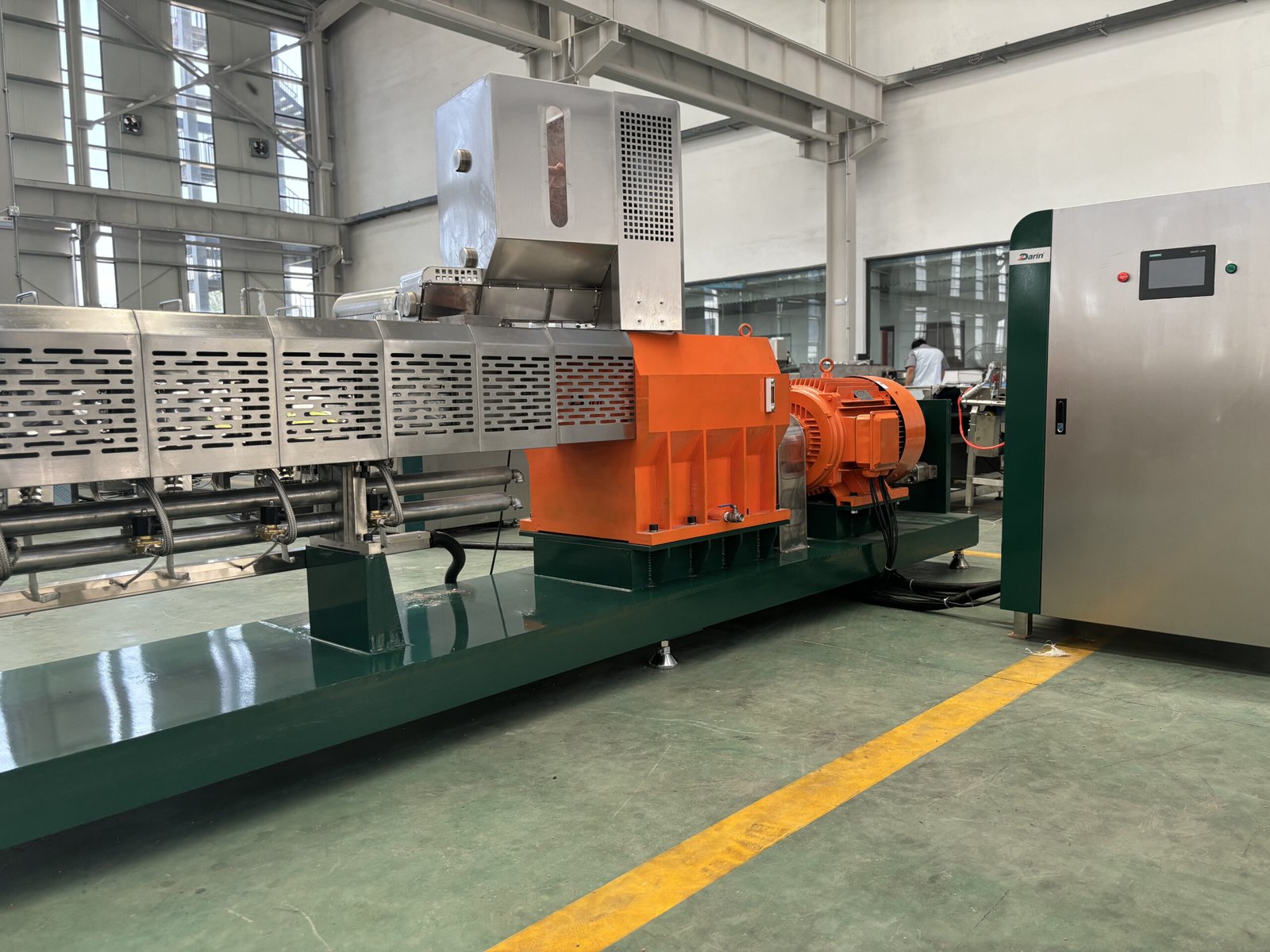

What Are the Future Trends and Innovations in Food Extrusion?
Emerging Technologies
- 3D Food Printing integrated with extrusion.
- Sustainable Extrusion using plant-based proteins.
- AI & Automation for process optimization.
Extrusion technology is evolving towards sustainability with lower energy consumption.True
New energy-efficient extruders reduce production costs and environmental impact.
Conclusion
Food extrusion is a vital process in modern food manufacturing, offering efficiency, consistency, and nutritional benefits. With advancements in technology, extrusion continues to evolve, enabling innovation in food production. If you're considering optimizing your pellet-based food production, investing in the right extrusion technology is key.
Want to Learn More? Contact Us!
Need expert guidance on food extrusion for pellets? Get in touch with our team today!
External Footnotes & References
This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of food extrusion for pellets, ensuring manufacturers understand its principles, benefits, and applications. Let me know if you need more details! 🚀










